Any electrical component will give off heat during operation. If an electrical part gains or loses too much heat, it will not function as it is intended to, which could cause numerous issues. There are multiple methods and devices to use for measuring electronic temperature.
Quick Navigation
- 4 Methods for Measuring Component Temperatures
- What Equipment Is Needed for Measuring Component Temperatures?
- Conduction vs. Convection for Cooling Power Supplies
- Request More Information From ACT Today
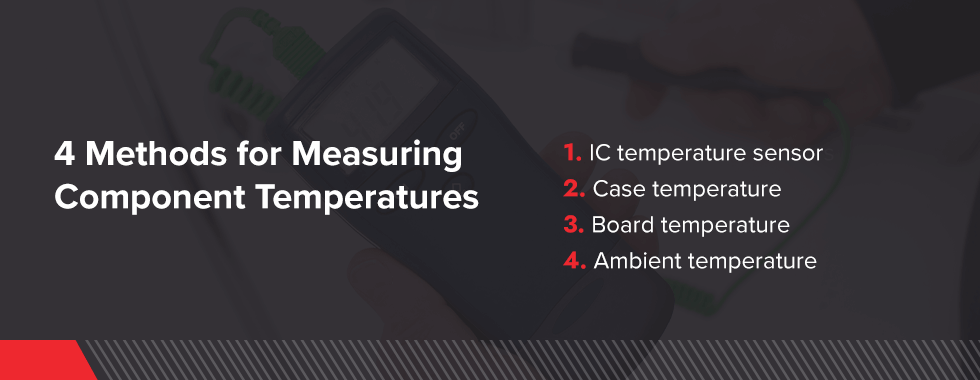
4 Methods for Measuring Component Temperatures
When you need to measure electrical component temperature, the four main ways are:
- IC temperature sensors: This sensor will produce a current in proportion to the temperature inside the piece. IC component sensors have a limited temperature range.
- Case temperature: You can take a reading in several ways, including using an infrared camera or gun or using a thermocouple.
- Board temperature: Use a thermocouple, infrared camera, or infrared gun to measure the board temperature.
- Ambient temperature: Get a temperature reading outside the component, usually via air or a controlled temperature. This method is typically less accurate than the others.
What Equipment Is Needed for Measuring Component Temperatures?
There are multiple types of temperature sensors used to measure the heat inside an electrical component, including:
- Thermocouple: These devices measure temperature through voltage.
- Resistive temperature measuring devices: This device measures temperature via resistance. As the temperature goes up, the resistance increases.
- Infrared sensors: These are noncontact temperature measuring devices. Often, infrared devices are handheld.
- Diode: These sensors are either permanently inside the component or a thermal test chip.
- Bimetallic measurement device: This device has two metals bonded together and measures the rate of their thermal expansion.
Conduction vs. Convection for Cooling Power Supplies
Cooling components is an integral part of ensuring they work as intended. To do this, you can either use conduction or convection cooling methods. In conduction cooling, heat moves away from one hot spot to another location. Cooling is completed through direct contact within the power supply using heat sinks and hot plates.
For convection cooling, natural air often removes heat from the device. You can usually complete this job naturally with the help of the device’s environment. However, forced convection cooling is another option where fans move air to reduce the heat inside the component.
Request More Information From ACT Today
ACT power supplies are cooled using either convection or conduction. Our team works with you to help you find which way suits your needs best. We also provide ongoing support throughout the product’s life cycle.
Our power supplies are reliable and affordable. Get in touch with us to find the power supply products you need today!
